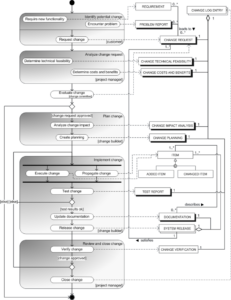
Utilizing such a form offers several advantages. It minimizes the risk of miscommunication and errors by providing a clear framework for requesting alterations. This clarity helps maintain version control and ensures all modifications are properly documented. Furthermore, it fosters better collaboration amongst team members and stakeholders, leading to more efficient project management and reduced development time. A systematic approach to change management ultimately contributes to higher quality deliverables and improved project outcomes.
This structured approach to design modification is crucial for various applications, from software development to engineering and construction. The following sections delve into specific use cases, best practices for implementation, and examples of effective forms.
Key Components of a Design Change Request
Effective management of design modifications requires a structured approach. A standardized form ensures all pertinent information is captured, facilitating efficient review and approval processes.
1. Identification: A unique identifier, such as a sequential number, distinguishes each request and aids in tracking.
2. Requestor Information: Details of the individual or team initiating the change, including name, department, and contact information, are essential for communication.
3. Date of Request: Recording the submission date establishes a timeline for processing the modification.
4. Description of Change: A clear and concise explanation of the proposed modification, including its purpose and scope, is crucial for understanding the request.
5. Rationale for Change: Justification for the modification, including the problem being addressed or the improvement being sought, clarifies the necessity of the change.
6. Impact Assessment: An evaluation of the potential effects of the change on the project, including cost, schedule, and resources, allows stakeholders to understand the implications.
7. Proposed Solution: Specific details of the proposed modification, including technical specifications and design documents, provide a clear picture of the intended implementation.
8. Approval Section: Space for signatures and dates from relevant stakeholders indicates formal authorization of the change.
These components provide a comprehensive framework for documenting, reviewing, and approving modifications, ensuring a controlled and traceable process for managing design changes.
How to Create a Design Change Request Template
Developing a standardized template for design change requests ensures consistency and efficiency in managing modifications throughout a project lifecycle. A well-structured template facilitates clear communication and informed decision-making.
1: Define Objectives: Clearly outline the purpose of the template and the types of design changes it will encompass. Consider project-specific requirements and industry best practices.
2: Determine Essential Fields: Identify the key information required to document a change request comprehensively. This typically includes an identifier, requestor information, date, description of the change, rationale, impact assessment, proposed solution, and approval sections.
3: Choose a Format: Select a suitable format for the template, such as a digital document or spreadsheet. Consider accessibility and ease of use for all stakeholders.
4: Structure the Layout: Organize the fields logically to facilitate readability and efficient completion. Group related information together and use clear headings.
5: Incorporate Version Control: Implement a mechanism for tracking revisions to the template itself. This ensures all users are working with the most up-to-date version.
6: Test and Refine: Pilot test the template with a small group of users to identify any areas for improvement. Gather feedback and refine the template based on user experience.
7: Train Users: Provide training to all stakeholders on how to properly complete and submit design change requests using the template. Clear instructions and examples promote consistent usage.
8: Regularly Review: Periodically review the template’s effectiveness and make necessary updates to align with evolving project needs and industry best practices.
A well-designed template, combined with consistent usage and regular review, establishes a robust process for managing design changes, contributing to successful project outcomes.
Standardized forms for requesting design modifications provide a crucial mechanism for managing change within projects. These structured templates ensure clear communication, facilitate comprehensive documentation, and enable informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. Key elements such as unique identifiers, detailed descriptions, rationale explanations, impact assessments, and approval sections contribute to a robust change management process. A well-defined process, supported by a properly implemented template, minimizes risks, improves collaboration, and ultimately enhances project outcomes.
Effective management of design changes is essential for project success. Organizations that prioritize and implement robust change control procedures, utilizing well-designed templates and consistent practices, position themselves for greater efficiency, reduced errors, and improved overall project quality. The consistent application of these principles strengthens project integrity and contributes to achieving desired objectives.