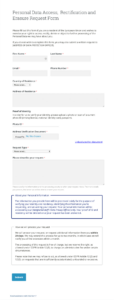
Utilizing a pre-designed structure for data access requests offers several advantages. It simplifies the process for requesters by providing clear guidance on the necessary information. This clarity can lead to faster processing times and reduce the likelihood of requests being rejected due to incomplete information. Organizations also benefit from the standardization, experiencing increased efficiency in managing and responding to these requests, minimizing administrative burden and potential legal complications.
This discussion will explore the core components of a well-drafted access request structure, examine best practices for their usage, and address common questions about the process. Further sections will delve into the legal framework surrounding data access rights and provide practical examples for various scenarios.
Key Components of a Data Access Request
Effective data access requests require specific information to ensure clarity and expedite processing. The following components are essential for a comprehensive request.
1: Requester Identification: Clear identification of the individual making the request is paramount. This typically includes full legal name, current address, and any previous names or addresses used while interacting with the organization holding the data.
2: Specific Data Sought: Requests should clearly specify the information being sought. Vague or overly broad requests may be rejected. Providing context or specific date ranges can be beneficial.
3: Proof of Identity: Organizations often require proof of identity to prevent unauthorized access to personal data. Acceptable forms of identification may include copies of passports, driver’s licenses, or other official documents.
4: Contact Information: Providing clear contact information, such as a phone number and email address, enables the organization to easily communicate updates or request clarification regarding the request.
5: Signature and Date: A signed and dated request demonstrates formality and confirms the requester’s intent. This can be a physical or digital signature, depending on the submission method.
6: Method of Delivery: Specifying the preferred method for receiving the requested information, such as email, postal mail, or secure online portal, streamlines the fulfillment process.
Accurate and complete information in these areas significantly contributes to efficient processing of access requests and ensures individuals receive the specific information they are entitled to access. These components serve as a foundation for clear communication and facilitate compliance with data protection regulations.
How to Create a Subject Access Request
Creating a comprehensive subject access request ensures efficient processing and increases the likelihood of receiving the desired information. The following steps outline the process of crafting an effective request.
1: Obtain a Template (Optional): While not mandatory, utilizing a template can streamline the process. Templates provide a pre-structured format, ensuring all necessary components are included. Numerous free templates are readily available online.
2: Clearly Identify the Requester: Begin by stating the requester’s full legal name, current address, and any previous names or addresses used while interacting with the organization.
3: Specify the Information Sought: Clearly and concisely detail the specific information being requested. Providing context, relevant dates, or specific file names can significantly aid the search process.
4: Include Proof of Identity: Attach a copy of a valid form of identification, such as a passport, driver’s license, or other government-issued identification. This verifies the requester’s identity and authorization to access the information.
5: Provide Contact Information: Include a current phone number and email address. This allows the organization to contact the requester for clarification or to provide updates on the request’s progress.
6: Sign and Date the Request: A signed and dated request formalizes the process and confirms the requester’s intent. Ensure the signature matches the identification provided.
7: Specify Preferred Delivery Method: Indicate the preferred method for receiving the requested information, such as email, postal mail, or secure online portal.
8: Submit the Request to the Correct Recipient: Identify the appropriate contact person or department within the organization responsible for handling data access requests. This information is typically available on the organization’s website or privacy policy. Submitting the request through the designated channels ensures timely processing.
Thorough preparation and attention to detail in crafting a subject access request contribute significantly to its efficient processing and successful outcome. Accurate and comprehensive information enables organizations to locate and provide the requested data promptly and effectively, facilitating transparency and upholding individual data rights.
Access to personal information held by organizations is a fundamental right. Leveraging readily available resources, such as pre-designed request structures, simplifies this process for individuals seeking to exercise this right. Understanding the key components of a comprehensive request, including clear identification, specific data identification, and proof of identity, significantly contributes to efficient processing and successful outcomes. This knowledge empowers individuals to engage confidently with their data rights and fosters transparency and accountability in data handling practices.
Ensuring individuals are aware of their data access rights and possess the tools to exercise these rights is crucial for maintaining trust and promoting responsible data governance. The availability of accessible templates and clear guidance empowers individuals to navigate the process effectively, fostering a culture of transparency and accountability within the broader data landscape. Continued efforts to streamline this process and enhance accessibility contribute significantly to upholding individual rights in the digital age.