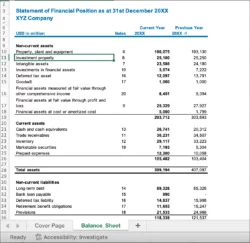
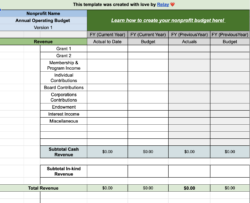
Securing funding for your project or organization often hinges on presenting a compelling grant proposal. While your mission and proposed activities are undoubtedly vital, the financial aspect, specifically your budget, can make or break your application. A well-crafted budget demonstrates fiscal responsibility, a clear understanding of your project’s needs, and ultimately, your capacity to achieve your goals effectively.
Navigating the intricacies of budget creation can feel overwhelming, especially when you are passionate about your cause but less experienced with financial planning for grants. This is where a robust `sample grant proposal budget template` becomes an invaluable tool. It offers a clear, organized framework, guiding you through each necessary category and helping you account for every potential expense, ensuring nothing crucial is overlooked.
This article will walk you through the essential components of a strong grant proposal budget, offering insights into what funders look for and how to articulate your financial needs clearly and convincingly. With the right approach, your budget will not just be a list of numbers, but a powerful narrative supporting your project’s success.
Understanding the Core Components of Your Grant Budget
A grant budget isn’t just about listing how much money you need; it’s about providing a detailed, justified breakdown of how those funds will be utilized to achieve the proposed project’s objectives. Funders want to see that you’ve thought through every aspect of your project’s financial needs and that your requests are both reasonable and directly tied to the work you plan to do.
Think of your budget as a financial roadmap. Each line item should clearly indicate what the money is for, how much is required, and how it contributes to the overall project. Transparency and accuracy are paramount here, as even minor discrepancies can raise red flags for reviewers. It is also an opportunity to show you understand the full scope of your project, from the initial planning stages to final reporting.
A typical grant budget categorizes expenses into distinct areas, making it easier for both you and the funder to understand where resources will be allocated. These categories ensure that you cover all bases, from the people doing the work to the supplies they need, and the administrative costs associated with running your program.
Personnel Costs
This section covers all expenses related to the individuals who will be working on your project. It is often the largest portion of any project budget. Be specific about roles, time commitments, and compensation rates.
Operating Expenses
These are the day-to-day costs essential for the project’s operation, distinct from personnel. They support the environment and resources needed for your team to function effectively.
Program Specific Costs
These expenses are unique to the activities of your particular project and vary greatly depending on the nature of your work. They represent the direct costs of delivering your services or producing your outcomes.
It is also crucial to distinguish between direct costs, which are directly attributable to the project, and indirect costs (sometimes called administrative or overhead), which are general operating expenses of the organization that support the project. Many funders have specific guidelines regarding indirect cost rates. Ensure your budget aligns with their requirements. Being thorough and transparent in outlining these components significantly boosts your proposal’s credibility.
Tips for Crafting a Winning Budget Narrative
While a detailed numerical budget spreadsheet is foundational, it’s only one part of the equation. The budget narrative is your opportunity to explain and justify every line item, bringing the numbers to life with clear, concise language. This narrative convinces funders that your budget is not just a wish list, but a carefully considered plan directly linked to achieving your project’s goals.
Your narrative should explain the necessity of each expense, demonstrating how it directly contributes to the project’s objectives. For instance, if you budget for a project coordinator, the narrative should explain their specific duties and how those duties are integral to the project’s success. This is where you connect the dots between your financial needs and your project’s impact.
Consistency between your project description, activities, and budget narrative is key. Reviewers will cross-reference these sections to ensure everything aligns. Any discrepancies can erode confidence in your proposal, so double-check that your narrative supports the numbers and that both accurately reflect the scope of work described elsewhere in your application.
Having a well-organized financial plan is a cornerstone of any successful grant application. By diligently utilizing a comprehensive `sample grant proposal budget template` and understanding what funders prioritize, you can present a budget that is not only accurate and transparent but also powerfully persuasive. It transforms a simple list of figures into a compelling argument for your project’s viability and potential for impact.
Investing the time to meticulously craft your budget and its accompanying narrative will significantly strengthen your overall proposal. It showcases your organizational prowess, demonstrates fiscal responsibility, and ultimately increases your chances of securing the funding needed to bring your valuable projects to fruition. Approach this critical section with confidence and clarity, and you will be well on your way to achieving your funding goals.