Utilizing such forms streamlines the process for both data subjects and organizations. For individuals, it clarifies the information needed to make a valid request, reducing potential back-and-forth communication. For organizations, it provides a standardized framework for handling requests, ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations and minimizing the risk of errors or delays. This ultimately fosters greater transparency and trust in data handling practices.
The following sections delve into the specific components of these forms, legal considerations, best practices for implementation, and available resources.
Key Components of a Data Access Request Form
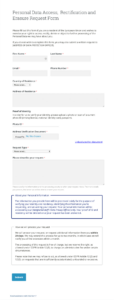
Effective data access request forms contain essential elements that facilitate clear communication and efficient processing. These components ensure that individuals can easily request their data, and organizations can readily understand and fulfill those requests.
1: Requester Identification: Clear fields for providing full legal name, contact information, and any other identifying details required by the organization are essential. This ensures requests are properly attributed and facilitates communication.
2: Specific Data Sought: The form should enable requesters to specify the exact information they seek. This may include categories of data, date ranges, or specific documents. Clear articulation prevents ambiguity and helps organizations pinpoint relevant information.
3: Preferred Response Format: Offering options for receiving the data, such as electronic copies, physical copies, or specific file formats, accommodates diverse needs and preferences. This enhances accessibility and usability.
4: Authorization and Verification: Mechanisms for verifying the requester’s identity, such as signature requirements or authentication processes, help prevent unauthorized access. This safeguards personal data and maintains security.
5: Submission Instructions: Clear guidance on how to submit the completed form, including designated contact points or online portals, ensures requests reach the appropriate channels efficiently.
6: Date of Request: Including a field for the date of the request allows for tracking and aids in meeting response deadlines established by data privacy regulations.
A well-designed form incorporating these elements promotes transparency, simplifies the request process, and helps organizations comply with legal obligations regarding data access rights.
How to Create a Subject Data Access Request Template
Developing a standardized form for subject data access requests requires careful consideration of legal requirements and practical usability. A well-crafted template facilitates efficient processing and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
1: Define Scope and Purpose: Clearly outline the types of data covered by the template and the intended audience. Consider specific regulatory requirements relevant to the organization’s jurisdiction and industry.
2: Structure and Format: Adopt a clear and logical structure for the template. Use concise language, headings, and subheadings to guide users through the required information. Ensure the format is accessible and user-friendly.
3: Incorporate Essential Elements: Include fields for requester identification, specific data sought, preferred response format, authorization and verification, submission instructions, and the date of the request. These components enable comprehensive and verifiable requests.
4: Legal Review and Compliance: Ensure the template aligns with applicable data privacy regulations. Seek legal counsel to review and validate the form’s content and compliance with jurisdictional requirements.
5: Accessibility and Language: Provide the template in accessible formats and multiple languages if necessary to accommodate diverse user needs. This promotes inclusivity and ensures equal access to information.
6: Testing and Refinement: Conduct thorough testing of the template with representative users to identify any areas for improvement. Gather feedback and refine the form to optimize usability and clarity.
7: Implementation and Training: Implement the finalized template through appropriate channels, such as online portals or designated contact points. Train staff on how to use and process requests submitted through the template.
8: Regular Review and Updates: Periodically review and update the template to reflect changes in regulations, organizational practices, or user feedback. This ensures the form remains effective and compliant over time.
By following these steps, organizations can create a robust and effective template that streamlines the data access request process, strengthens data protection efforts, and fosters trust with data subjects.
Standardized forms for accessing personal data represent a crucial element of modern data governance. These templates facilitate the exercise of individual rights while offering organizations a structured framework for managing requests efficiently and transparently. Key components, such as clear identification requirements, specific data descriptions, and secure submission processes, ensure both accuracy and security. Proper implementation, including legal review and ongoing refinement, is essential for maximizing effectiveness and maintaining compliance with evolving data privacy regulations.
Effective management of data access requests fosters trust, promotes accountability, and contributes to a more responsible data ecosystem. Organizations must prioritize the development and implementation of robust procedures, recognizing that providing individuals with control over their personal information is not just a legal obligation, but a fundamental aspect of ethical data handling.