Utilizing such a structure streamlines the request fulfillment process, reducing errors caused by miscommunication or incomplete information. This, in turn, can lead to improved efficiency in service delivery, better resource allocation, and enhanced user satisfaction. Standardized requests also facilitate tracking and reporting on service requests, contributing to valuable insights for process improvement.
This structured approach is beneficial in various contexts, ranging from troubleshooting hardware and software issues to requesting new software installations, access permissions, or system modifications. The following sections will explore these applications in greater depth.
Key Components
Effective management of IT service requests relies on well-defined, consistently structured information. Essential components ensure clarity, completeness, and efficient processing.
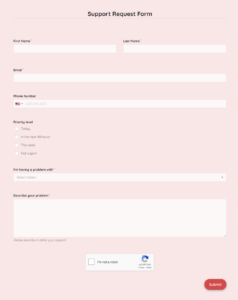
1. Requester Information: Clear identification of the individual making the request, typically including name, department, contact information, and potentially employee ID.
2. Date and Time of Request: Timestamping the request allows for tracking, prioritizing, and reporting on service level agreements.
3. Request Type: Categorizing the request (e.g., hardware, software, access, etc.) facilitates routing and assignment to appropriate support teams.
4. Subject/Title: A concise, descriptive subject line enables quick understanding of the request’s nature.
5. Description: A detailed explanation of the issue, service required, or desired outcome. This section should include specific details, error messages, steps to reproduce the problem, and any relevant background information.
6. Priority Level: Indicates the urgency of the request (e.g., critical, high, medium, low) to guide response times and resource allocation.
7. Supporting Documentation: Any relevant attachments, such as screenshots, error logs, or supporting files, that can aid in understanding and resolving the issue.
8. Desired Outcome/Resolution: Specifies the expected result of the request, clarifying expectations for both the requester and the support team.
These elements provide a framework for consistent and effective communication, contributing to improved service delivery and issue resolution. Complete and accurate information facilitates efficient processing and allows support teams to address requests promptly and effectively.
How to Create a System Service Request Template
Developing a standardized template ensures efficient and effective handling of service requests. A well-designed template facilitates clear communication, reduces errors, and streamlines the request fulfillment process. The following steps outline a structured approach to template creation.
1. Define Scope and Purpose: Determine the types of service requests the template will cover. Consider specific needs and common request categories within the organization.
2. Identify Required Information: List essential data points necessary for processing requests, including requester details, request type, description, priority, and desired outcome. Ensure alignment with existing ticketing systems or workflows.
3. Select a Format: Choose a suitable format, such as a web form, word document, or spreadsheet. Consider accessibility, ease of use, and integration with other systems. Web forms offer advantages in terms of automation and data collection.
4. Design the Template: Structure the template logically, using clear labels and instructions. Group related fields together and ensure mandatory fields are clearly marked. Prioritize a clean, easy-to-understand layout.
5. Implement Input Validation: Incorporate mechanisms to validate data input, such as required fields, data type checks, and character limits. This helps ensure data integrity and reduces errors.
6. Test and Refine: Conduct thorough testing with representative users to identify any usability issues or areas for improvement. Iterate based on feedback to optimize the template’s effectiveness.
7. Deploy and Communicate: Make the template readily accessible to all users. Provide clear instructions on how to use the template and communicate its purpose and benefits.
8. Monitor and Review: Regularly monitor the template’s usage and effectiveness. Gather feedback from users and support staff to identify opportunities for ongoing improvement and ensure it remains aligned with evolving needs.
A well-designed template, implemented effectively, promotes clear communication, reduces processing time, and improves the overall efficiency of service request management. Consistent usage and regular review contribute to continual refinement and optimization.
Standardized request procedures, facilitated by well-designed templates, are crucial for efficient management of IT services. Templates ensure consistent communication, reduce errors stemming from incomplete information, and streamline request processing, ultimately contributing to improved service delivery and resource allocation. Effective templates incorporate key elements such as clear requester identification, detailed descriptions, prioritized urgency levels, and supporting documentation. Furthermore, ongoing review and refinement of these templates ensure they remain aligned with evolving organizational needs and technological landscapes.
Organizations seeking to optimize IT service management must prioritize the development and implementation of comprehensive service request templates. This structured approach fosters clear communication, reduces resolution times, and enhances user satisfaction. Embracing standardized request procedures contributes to a more proactive and efficient IT support environment, laying the groundwork for continuous service improvement and enhanced operational effectiveness.