Understanding the structure and application of these forms is crucial for effectively managing change within any organization. The following sections will delve deeper into the key components, best practices, and practical examples of their usage in diverse contexts.
Key Components of a Change Request Form
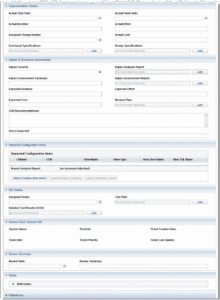
Effective change management relies on capturing comprehensive information about proposed modifications. A well-designed form includes several essential elements to ensure clarity, traceability, and appropriate approvals.
1. Requestor Information: Clear identification of the individual or team initiating the request, including contact details, is crucial for communication and accountability.
2. Date of Request: Timestamping the submission provides a chronological record for tracking and reporting.
3. Change Description: A detailed explanation of the proposed modification, including its purpose and scope, is essential for understanding the nature of the change.
4. Justification: A clear rationale explaining the business need for the change, including potential benefits and expected outcomes, is necessary for informed decision-making.
5. Impact Assessment: An analysis of potential effects on existing systems, processes, and stakeholders helps to anticipate and mitigate risks.
6. Implementation Plan: A detailed outline of the steps involved in implementing the change, including timelines, resources, and responsibilities, ensures a structured approach.
7. Backout Plan: A contingency plan outlining steps to reverse the change in case of unforeseen issues minimizes potential disruption.
8. Approval Section: Designated spaces for relevant stakeholders to authorize the request ensures proper governance and accountability.
These components facilitate a thorough evaluation of proposed modifications, promoting informed decision-making and minimizing potential disruption from poorly planned changes. A complete and accurate form contributes to a smoother, more controlled change process.
How to Create a Change Management Request Template
Developing a robust template requires careful consideration of organizational needs and established change management processes. A well-structured template facilitates clear communication, efficient processing, and effective implementation of modifications.
1. Define Scope and Purpose: Clearly outline the types of changes the template will cover. Consider the specific needs of different departments or projects. A focused approach ensures relevance and usability.
2. Identify Key Stakeholders: Determine who needs to be involved in the change process, including requestors, approvers, implementers, and affected parties. Understanding roles and responsibilities ensures appropriate engagement.
3. Determine Required Information: Specify the essential data points needed to evaluate and implement changes effectively. This includes requestor details, change descriptions, justification, impact assessments, and implementation plans.
4. Design the Form Structure: Organize the information logically and clearly, using headings, subheadings, and tables for readability. A well-structured layout promotes efficient completion and review.
5. Establish Approval Workflows: Define the approval hierarchy and routing process. Ensure that appropriate stakeholders review and authorize changes based on their level of authority.
6. Implement Version Control: Maintain a record of template versions to track revisions and ensure consistency. Version control facilitates clarity and traceability throughout the change lifecycle.
7. Train Users: Provide training and guidance on how to use the template effectively. Clear instructions and practical examples ensure consistent application and reduce errors.
8. Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review the template’s effectiveness and make necessary updates based on user feedback and evolving organizational needs. Continuous improvement ensures relevance and optimal performance.
A well-designed template, incorporating these elements, provides a standardized framework for managing changes, leading to improved communication, reduced risks, and more successful implementations. Regular review and adaptation of the template to evolving organizational needs ensure its continued effectiveness.
Effective management of modifications within any organization requires a structured and standardized approach. A formalized submission process, supported by a comprehensive form, ensures that all proposed alterations are thoroughly documented, assessed, and approved. This structured methodology minimizes risks, enhances communication, and increases the probability of successful implementation. Key components of such a form include detailed descriptions of the proposed changes, justifications for their necessity, impact assessments, implementation plans, and clear approval processes. Implementing and adhering to these practices fosters a culture of controlled and well-managed evolution.
Organizations seeking to improve their change management practices should prioritize the development and implementation of a robust, standardized request procedure. This investment in structured processes contributes to greater agility, reduced disruption, and improved outcomes when implementing necessary modifications. By embracing a proactive and organized approach to change, organizations position themselves for greater success in navigating the evolving demands of the modern business landscape.