Utilizing a pre-designed format streamlines the application process, ensuring all necessary information is included, thereby increasing the likelihood of a favorable outcome. This organized approach saves time and effort for both the applicant and the reviewing authority. Furthermore, it promotes transparency and consistency in the handling of such requests.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components of these applications, offer guidance on completing them effectively, and explore various scenarios where they are commonly employed.
Key Components
Effective applications for exceptions to established rules require specific information presented in a clear and concise manner. The following components are typically essential:
1. Applicant Information: Clear identification of the individual or entity seeking the exception is crucial. This typically includes full name, contact information, and any relevant identifying numbers.
2. Specific Rule or Requirement: Precise identification of the specific rule, regulation, or requirement from which an exception is sought is essential. This requires citing the specific code, section, or policy.
3. Rationale for Variance: A detailed explanation of the reasons necessitating the exception is critical. This should clearly articulate the circumstances making adherence to the standard rule impractical or unduly burdensome.
4. Proposed Alternative Solution: A clear description of the proposed alternative approach that will be implemented in lieu of the standard rule is necessary. This should demonstrate how the alternative will achieve a comparable or superior outcome.
5. Supporting Documentation: Any relevant documentation supporting the request, such as evidence of hardship, technical specifications, or expert opinions, strengthens the application.
6. Impact Assessment: An analysis of the potential impact of granting the exception, including any potential effects on safety, the environment, or other stakeholders, provides a comprehensive overview of the implications.
7. Timeframe: Specifying the desired duration of the exception, whether temporary or permanent, clarifies the scope of the request.
Providing comprehensive and well-supported justifications for each of these elements significantly increases the likelihood of a successful outcome. A complete application demonstrates a clear understanding of the rules and a commitment to finding a viable alternative solution.
How to Create a Request for Variance Template
Creating a standardized template ensures consistency and efficiency in handling requests for exceptions to established rules. A well-designed template guides applicants through the process, facilitating complete and well-structured submissions.
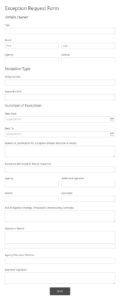
1. Header: The template should begin with a clear header identifying it as a “Request for Variance.” This section should also include space for the date of submission.
2. Applicant Identification: Fields for applicant details, including name, address, contact information, and any relevant identification numbers, should be included.
3. Rule or Requirement Citation: A dedicated section for specifying the exact rule or requirement from which variance is sought is essential. This includes the specific code, regulation, or policy number.
4. Justification: A designated area for explaining the reasons for the variance request is crucial. This section should prompt applicants to provide a detailed and compelling rationale.
5. Proposed Alternative: A section to outline the proposed alternative solution or approach should be included. This allows applicants to detail their proposed alternative and demonstrate its viability.
6. Supporting Documentation: The template should clearly indicate where supporting documentation should be attached or uploaded. This might include evidence of hardship, technical data, or expert opinions.
7. Impact Assessment: Including a section for assessing the potential impacts of granting the variance, such as safety, environmental, or economic considerations, promotes comprehensive evaluations.
8. Timeframe: A field to specify the requested duration of the variance, whether temporary or permanent, should be included.
9. Signature and Date: Space for the applicant’s signature and date signifies agreement with the provided information. This also serves as a formal record of the request.
A comprehensive template facilitates a clear and consistent process for requesting and reviewing variances, ensuring all necessary information is readily available. This structure benefits both applicants and reviewing bodies by streamlining the process and promoting informed decision-making.
Standardized forms for requesting exceptions to established rules provide a structured framework for seeking regulatory flexibility. Understanding the components of a well-crafted application, including clear identification of the rule, compelling justification, proposed alternatives, and supporting documentation, is crucial for a successful outcome. Developing and utilizing a comprehensive template ensures consistency and efficiency in the application and review process.
Effective management of variance requests promotes balanced adherence to regulations while accommodating justifiable deviations. Careful consideration of potential impacts and adherence to established procedures are essential for maintaining regulatory integrity and ensuring fair and transparent decision-making. This approach facilitates adaptability within a regulated environment, allowing for necessary flexibility while upholding established standards.